Indexing and Slicing
Contents
Indexing and Slicing#
Indexing and slicing is a crucial component of data science, but is one that we’ve watched students find difficult in the past. Try to think carefully about what is going on here as we go through the examples and exercises, we definitely be using this a lot going forward, and will be using it extensively in MATLAB in TB2 as well!
import numpy as np # we will be using numpy via the abbreviation np
data = np.array([1, 2, 3])
We can visualise the indicing and slicing of an array data as follows:
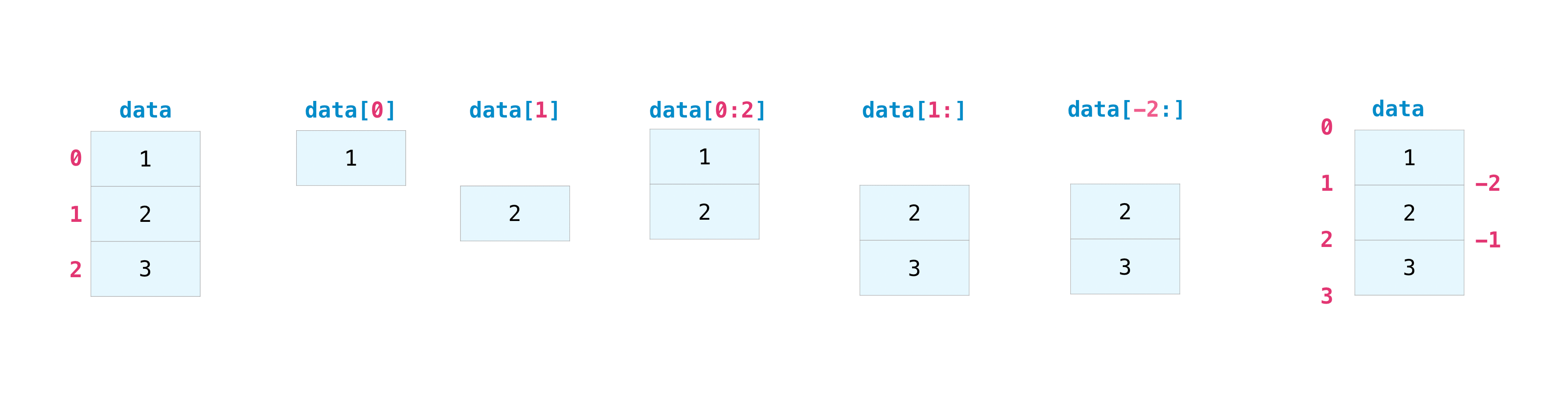
To explain what each of these are doing in turn:
data = np.array([1,2,3]) creates the array we will use for illustration
data[0] takes the first element of the array (remember python counts from 0!)
data[1] takes the second element of the array.
data[0:2] takes all values in data between 0 and 2, including the value at point 0 and not including the value at point 2.
data[1:] takes all values in data from point 1 until the end of the array.
data[-2:] Note the negative number here! This indicates that it is the second-from-last value. So it takes all values in data from the point second-from-last until the end.
data or data[:] will return all values in data.
print(data[0])
print(data[1])
print(data[0:2])
print(data[1:])
print(data[-2:])
print(data)
1
2
[1 2]
[2 3]
[2 3]
[1 2 3]
Let’s explore this in more detail, with more examples!
Slicing works as follows:
array[start:stop:step]
example_data = np.array([1, 5, 8, 4, 3, 6, 3, 7, 4, 6, 8, 9])
start = 2
stop = -3
step = 2
print(example_data[start:stop:step])
[8 3 3 4]
This example example_data[start:stop:step] would take every step value in example_data between start and stop.
This example example_data[2:-3:2] would take every second (or every other) value in example_data between the third point in the array and the third point from the end (not including the point that is third from the end).
Exercise 3.1A#
Create an array of first 100 positive integers (starting from \(1\)). Then use slicing to halve this array and get the first 50 positive integers. After that print every 3-rd element of the resulting array.
Exercise 3.1B#
Create an array which is [2**0, 2**1, 2**2, 2**3, 2**4, ... 2**10] you can do this by:
First create an array of integers between 0 and 10 inclusive (called
my_array)Compute
2**my_array
Then slice this array to contain only the 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th entries.
Exercise 3.1C#
Create the following list of numbers as a numpy array
[1, 3.4656, 4, 8.23423, 9, 3.3424, 16, 32.5465, 25, 23.435, 36, 34.65567]
and slice the array to take every other value starting from the first (so the first, third, fifth …) values
Filtering arrays via a condition#
If you wish to select certain values of a numpy array that fulfil a certain condition, then numpy is again very useful!
FOr example if we want all values in an array that are bigger than 40:
example_array = np.array([1, 40, 50, 100, 90])
print(example_array[example_array > 40])
[ 50 100 90]
This does not work on regular python lists. Try running the cell below to check this.
example_list = [1, 40, 50, 100, 90]
print(example_list[example_list > 40])
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Input In [6], in <module>
1 example_list = [1, 40, 50, 100, 90]
----> 2 print(example_list[example_list > 40])
TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'list' and 'int'
Exercise 3.2#
Please evaluate the cell below.
array_with_some_numbers = np.random.randint(0, 100, size=100)
In the cell below write a condition that prints all the numbers from this array that are greater than 50.
In the cell below write a condition that prints all numbers from array_with_some_numbers that are less than 10.
Creating subsamples of an array#
You can use or and and, with or being | and and being &. This is a common method for creating subsamples of a larger data array for analysis, and potentially very powerful for project work.
print(example_array[(example_array > 40) & (example_array <= 90) ])
[50 90]
print(example_array[(example_array < 40) | (example_array > 90) ])
[ 1 100]
Exercise 3.3#
In the cell below please filter the values from the array from Exercise 3.2 so that you create an array of elements which are greater than \(10\) and smaller than \(20\).
The expressions that we insert in the square bracket return an array of True/False statement that matches the position of the array that has been used.
example_array > 40
array([False, False, True, True, True])
(example_array > 40) & (example_array <= 90)
array([False, False, True, False, True])
(example_array < 40) | (example_array > 90)
array([ True, False, False, True, False])


